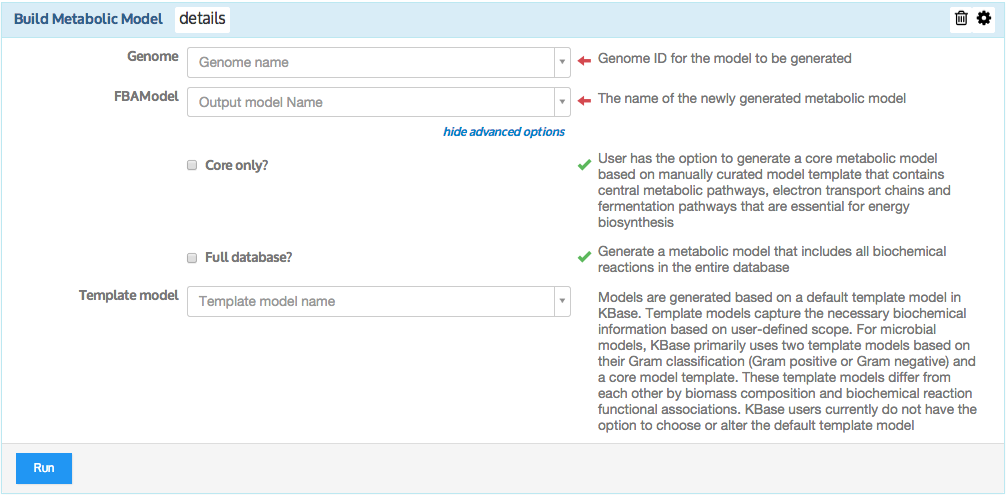
Generate a draft metabolic model based on an annotated genome.
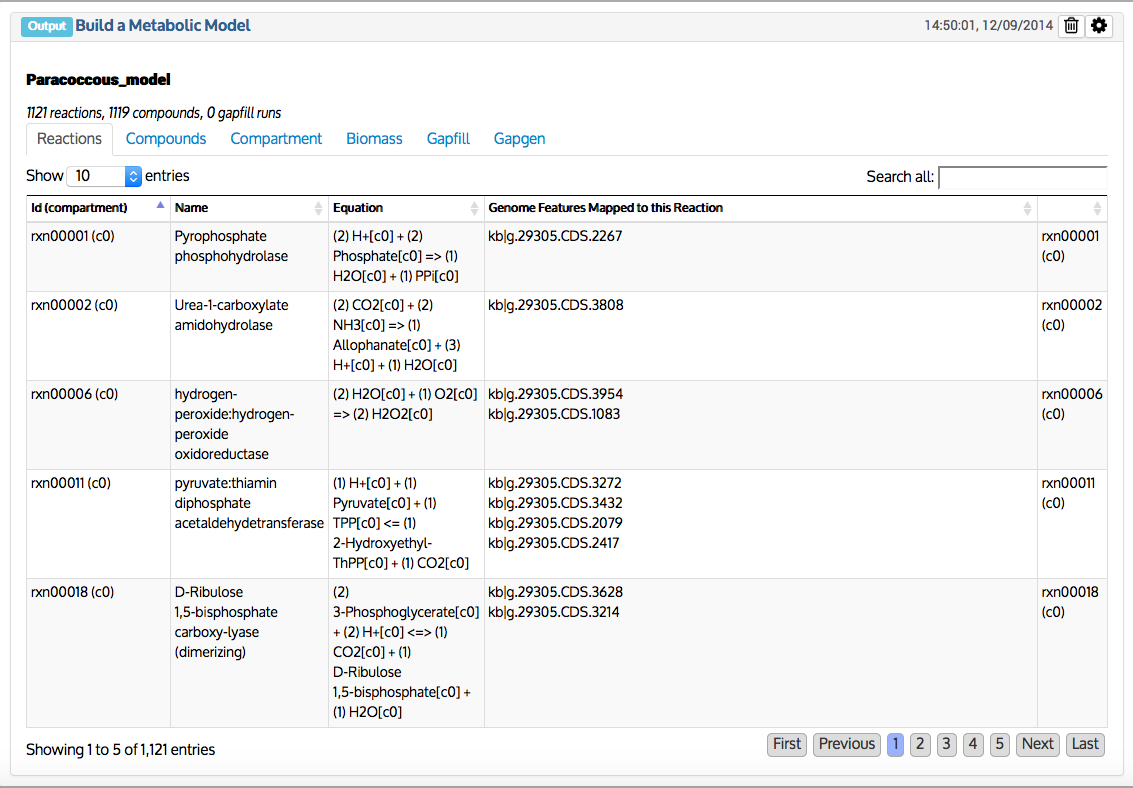
This app takes an annotated metagenome assembly object (output object produced from Annotate Metagenome Assembly and Re-annotate Metagenomes with RASTtk - v1.073 app - see https://narrative.kbase.us/#appcatalog/app/RAST_SDK/annotate_metagenome/beta) and produced a draft metabolic model that represents the overall physiology of the metagenome. The metabolic reactions are derived based on RAST annotations, where RAST functional roles are used as a controlled vocabulary to derive relevant biochemistry. Therefore, it is essential to have the RAST annotations populated prior to building a draft metagenome model. The metagenome model is a representation of all the metabolic pathways encoded by the genes of all microbial organisms (prokaryotes in this case) that may exist in the metagenome. Thus, a metabolic model always includes a stoichiometric matrix of metabolic reactions and their associated biochemical compounds. Models also include data specifying how each reaction depends upon the genes encoding it, called gene-protein-reaction (GPR) associations. The GPR associations in a model allow it to differentiate between cases where protein products from multiple genes form a complex to cooperatively catalyze a reaction, and cases where protein products from multiple genes can independently catalyze the same reaction. Finally, in general, models typically include a biomass objective function, which indicates the relative abundance of small molecule building blocks (e.g. amino acids, lipids, energy, cell-wall materials, quinones ) that a cell must produce from available nutrients to grow and survive. In the context of metagenome models, we use the same biomass components that are typically used for isolate specific models.
Optional Inputs:
Reads Coverage: The app can optionally take the reads coverage and computes the coverages against the metagenome assembly, then stores the coverages in the model as reaction coverages and as contig coverages. This coverage information could be useful in downstream analysis apps that; where the metagenome is analyzed against the extracted bins, the coverage data would easily propagate onto individual bins identifying relative abundance of contigs (organisms) or metabolic pathways (at the reaction level).
Gapfilling media and Gapfill model: Although this is an optional input it is set to be 'true' by default as be recommended to execute by default (Gapfill model checkbox). Typically the draft metabolic models are incomplete due to knowledge gaps. To simulate models (e.g.; run FBA for cell growth), the gaps need to be filled and complete. (Learn more about gap-filling please refer to Gapfill Metabolic Model App.) The user has the option to un-check the Gapfilling option, where the resulting draft metagenome model is based solely on RAST annotations. Reactions to be used by gapfilling algorithm are selected from the Model SEED biochemistry database. This curated database contains mass and charge-balanced reactions, standardized to aqueous conditions at neutral pH. The Model SEED reaction database integrates biochemistry contained KEGG, MetaCyc, EcoCyc, Plant BioCyc, Plant Metabolic Networks, and Gramene.
Team members who developed & deployed algorithm in KBase:Chris Henry, Janaka Edirisinghe, Sam Seaver, Neal Conrad. For questions, please contact us.
Related Publications
- [1] Henry CS, DeJongh M, Best AA, Frybarger PM, Linsay B, Stevens RL. High-throughput generation, optimization and analysis of genome-scale metabolic models. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28: 977 982. doi:10.1038/nbt.1672 , https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20802497
App Specification:
https://github.com/cshenry/fba_tools/tree/b083384ac00d4f9d7cb796a664ee3ffd017cf248/ui/narrative/methods/build_metagenome_modelModule Commit: b083384ac00d4f9d7cb796a664ee3ffd017cf248