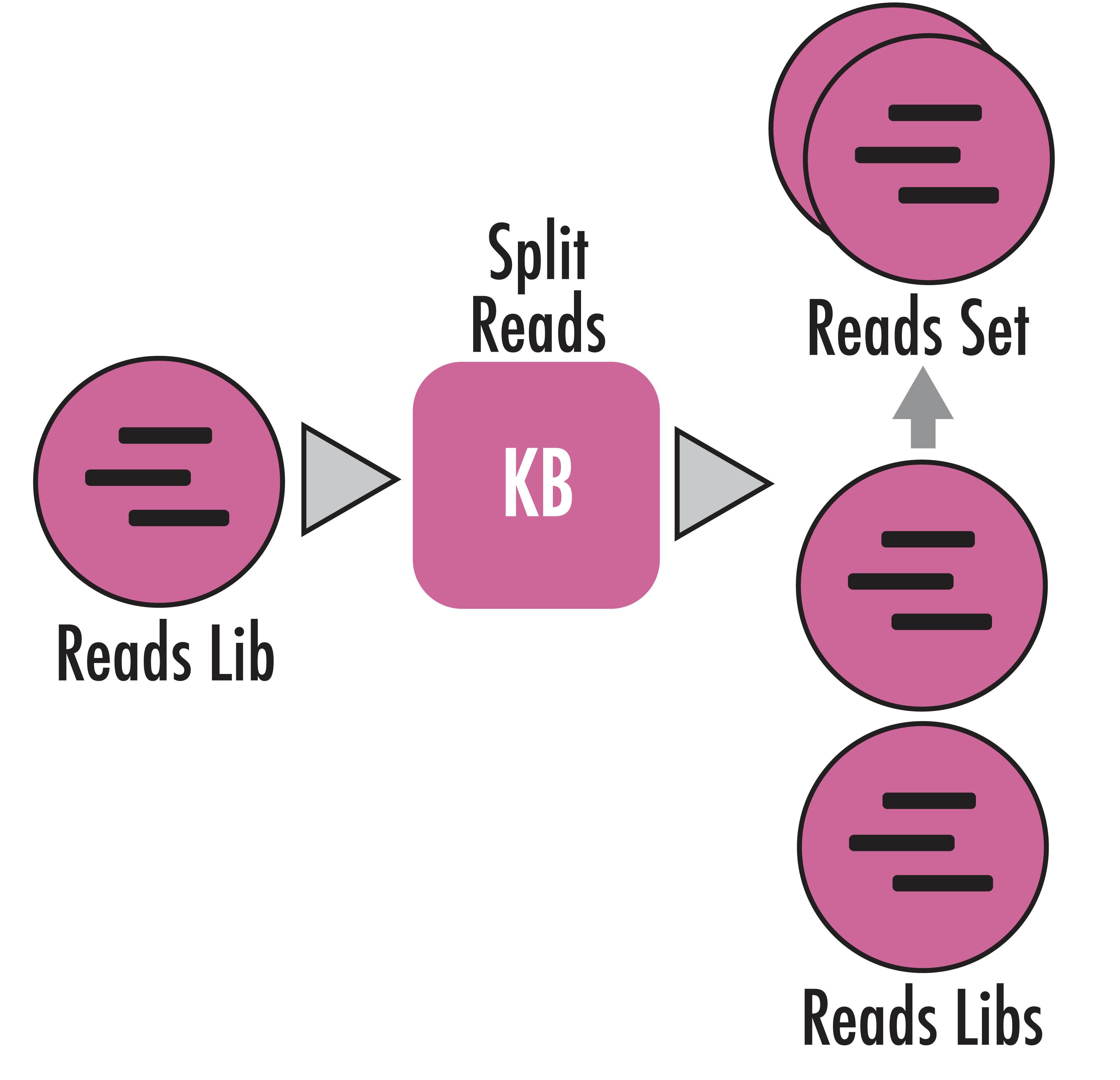
Split a Reads Library into smaller, evenly sized Reads Libraries.
This App allows the user to split a Reads Library into evenly sized Reads Libraries, organized into a Reads Set. Smaller read libraries can be used for running faster tests and parameter discovery for Apps such as quality trimming, assemblers, read aligners, taxonomic and functional classifiers and profilers, and RNA-Seq Apps. Additionally, splitting a single large library into smaller non-overlapping libraries creates technical replicates that allow a researcher to perform replicate analyses in the case that they don t have biological replicates.
All created sub-libraries are evenly-sized but may be off by one sequence if the split number does not evenly divide the number of source reads. In other words, all sequences in the source library will wind up in one of the sub-libraries. Read records are assigned one at a time in turn to the sub-libraries, so the resulting split libraries are taken evenly from the whole input library, not as uninterrupted chunks from the source. This means that if you split the source library into three sub-libraries the first, fourth, seventh (and so on) sequences in the source library will be placed in the first sub-library, the second, fifth, eighth (and so on) sequences will be placed in the second sub-library, and the third, sixth, ninth (and so on) sequences in the third sub-library. Additionally, the output sub-libraries will be organized into a corresponding ReadsSet object, which is named by the user.
Configuration
- Reads Library: This is the source Reads Library. It can be Single-End or Paired-End. PairedEndLibraries use the read ID to correlate the mated forward and reverse reads, and must have a mate pair for all records. If you are uncertain about whether or not this requirement ismet, you should run Trimmomatic or another App that will produce a PairedEndLibrary object that only contains mated pairs.
- Description: Describe the contents of the output ReadsSet.
- Split Number: This value should be based on the needs of your analysis and the size of the source Library. Obviously, larger libraries can be split more times and still produce reasonably-sized sub-libraries. Avoid producing exceptionally small sub-libraries as the analysis can suffer. Highly divergent technical replicate analysis can indicate this is a problem. The default value is 10, but for some replicate analysis, the user may wish to use a value of 3 (depending on the expectations of the protocol).
- Output Reads Set: Sub-library objects are given names automatically based on the name of the source library. However, the user provides the name of the ReadsSet object that contains the sub-library objects.
Team members who developed & deployed App in KBase: Dylan Chivian. For questions, please contact us.
Related Publications
- Arkin AP, Cottingham RW, Henry CS, Harris NL, Stevens RL, Maslov S, et al. KBase: The United States Department of Energy Systems Biology Knowledgebase. Nature Biotechnology. 2018;36: 566. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4163 , https://www.nature.com/articles/nbt.4163
App Specification:
https://github.com/kbaseapps/kb_ReadsUtilities/tree/de8955d0a9f373bff40882a02cd7742aa7560eea/ui/narrative/methods/KButil_Split_ReadsModule Commit: de8955d0a9f373bff40882a02cd7742aa7560eea