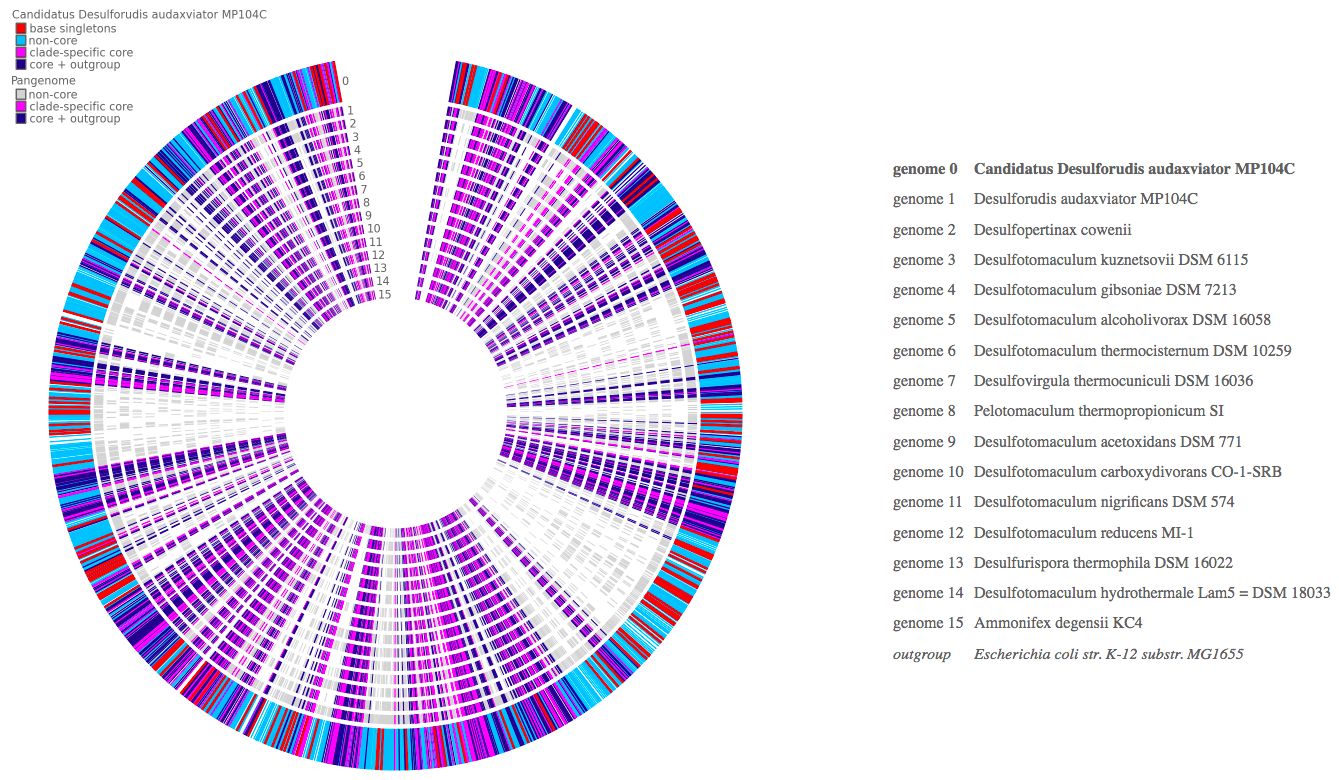
View a microbial Pangenome as a circle plot.
After performing a Pangenome calculation, you can use this App to view the overlapping membership of genes against a base genome. Additionally, this App will split the Pangenome into Feature Sets corresponding to the Core, Clade-specific Core, Singleton, and Partial (non-core & non-singleton fraction) pangenomes.
Pangenome Categories
The Pangenome represents the collection of all genes found in a collection of related organisms, grouped by sequence homology. Methods like OrthoMCL attempt to distinguish which genes are true orthologs and vertically inherited as opposed to lineage derived paralogous expansions by duplication. Homologous gene collections are typically categorized into Core, Clade-specific Core, and Singleton, with the remaining ortholog sets just considered the rest of the Pangenome (here termed the Partial Pangenome ).
Core: Those ortholog sets with at least one gene from the ortholog set with a gene in each of the genomes. It is most likely that the common ancestor of the species clade contained the ancestral form of the gene that each of the modern genomes inherited. Furthermore, given that the gene has been retained by all of the modern species, it is likely required, or at least sufficiently beneficial to lifestyle, to be retained. The rule used by Pangenome Circle Plot to determine if a homolog set should be considered Core is that a gene is found in all N genomes. When using incomplete genomes, the 100% presence rule may be too strict given that the gene may exist but not be observed. Rather than impose flexible thresholds for presence, we recommend instead that the user only include the most complete genomes possible in pangenome calculations.
Clade-specific Core: Core gene ortholog clusters contain functions that are universal to all life and therefore one often wishes to separate out those housekeeping functions from those which characterize the core function of a given clade. To accomplish this, one should include a distinct outgroup species in the Pangenome calculation, either distinguished by its lack of a given functionality and/or phylogenetically distant (e.g. Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 if one is calculating the Pangenome for a set of Clostridia). The outgroup distance shouldn t be so great that orthology calculations are likely to fail due to sequence divergence being too great (e.g. Archaea should not be used as outgroups for Bacterial pangenomes). This App includes an optional field to specify which genomes in the input Pangenome obect should be considered outgroups and, if provided, will split the Core fraction of the Pangenome into Clade-specific Core and Non-specific Core. The rule used is Non-specific Core is present in all genomes, whereas Clade-specific Core is present in all but the outgroup genomes.
Singleton: The Pangenome calculation will find a large number of genes with no sequence homology to genes in any other genomes. These are categorized as Singletons. The rule is presence in one and only one genome. They may represent generation of novel functions, horizontal transfer from distal lineages not included in the Pangenome calculation, or missing proximal lineages that perhaps should have been included in the Pangenome calculation. If the set of genomes in the Pangenome calculation contains a broad phylogenetic sampling of the clade of interest, then the last candidate hypothesis is less likely.
Partial Pangenome: In between Core and Singleton are those ortholog clusters present in more than one genome and fewer than all. If using incomplete genomes, these sets may contain ortholog clusters that would otherwise be calculated as core functions, so exercise caution when using incomplete genomes (absence of evidence is not evidence of absence!). Whether these functions are introduced into a branch of the lineage or represent fluctuating capabilities of the clade can be determined by placing the Pangenome Analysis against the Species Tree using the related App Phylogenetic Pangenome Accumulation.
Configuration
Base Genome: The base Genome is used to order the ortholog clusters into a ring in the output visualization, following the order of the genes in the base genome. The order of the genes in the rest of the pangenome is aligned to the position of its ortholog in the base genome. The base genome must be one of the genomes in the pangenome object. Only one genome can be used as the base.
Pangenome: The pre-calculated pangenome object (containing the orthology relationships between the genes) to use for the visualization. Only one pangenome object can be used.
Custom Compare Genome(s): [advanced] The default behavior is to show all the genomes in the pangenome object, as well as use all of them for the Core, Singleton, etc. calculations. However, one can select only a subset of the genomes in the Pangenome object for visualization and Pangenome breadth calculation. By definition, the Base Genome will be included in the calculation, and one or more additional genomes can be added here. Just click on the "+" symbol to add each Genome object you wish to include in the Pangenome comparison.
Outgroup Genome(s): [advanced] As discussed above, one may add one or more outgroup genomes to split the calculation of the Core set to split Clade-specific from Non-specific Core. Any outgroup Genomes must have been among the genomes included previously in the creation of the Pangenome object.
Save Pangenome FeatureSets: FeatureSets containing Core (with outgroup Genome(s) this will be split into Clade-specific Core and Non-specific Core), Singleton, and Partial Pangenome (see above) gene members from the ortholog clusters are created if this option is set.
Team members who developed & deployed App in KBase: Dylan Chivian, using Pangenome Calculator OrthoMCL. For questions, please contact us.
Related Publications
- Li L, Stoeckert CJ, Roos DS. OrthoMCL: Identification of Ortholog Groups for Eukaryotic Genomes. Genome Res. 2003;13: 2178 2189. doi:10.1101/gr.1224503 , https://genome.cshlp.org/content/13/9/2178
App Specification:
https://github.com/kbaseapps/kb_phylogenomics/tree/7a7953cfae374968499ac49d7716ce9bc99b2ca0/ui/narrative/methods/view_pan_circle_plotModule Commit: 7a7953cfae374968499ac49d7716ce9bc99b2ca0