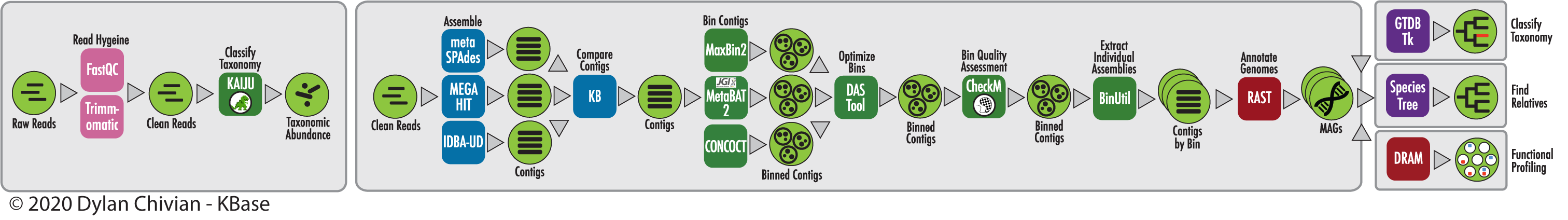
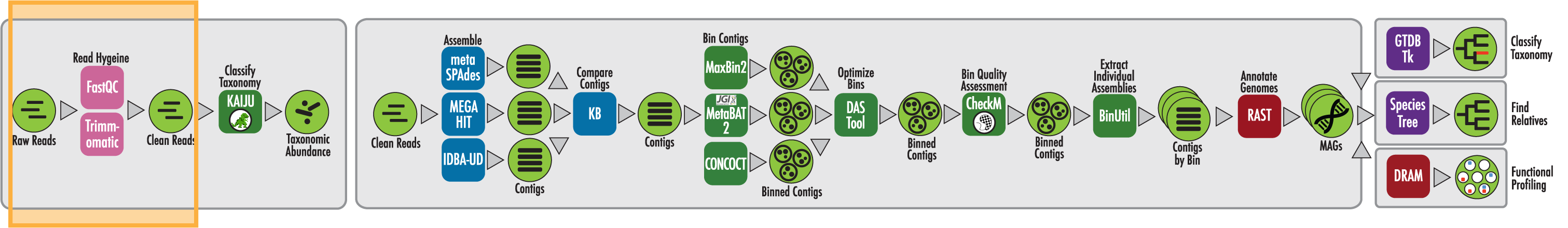
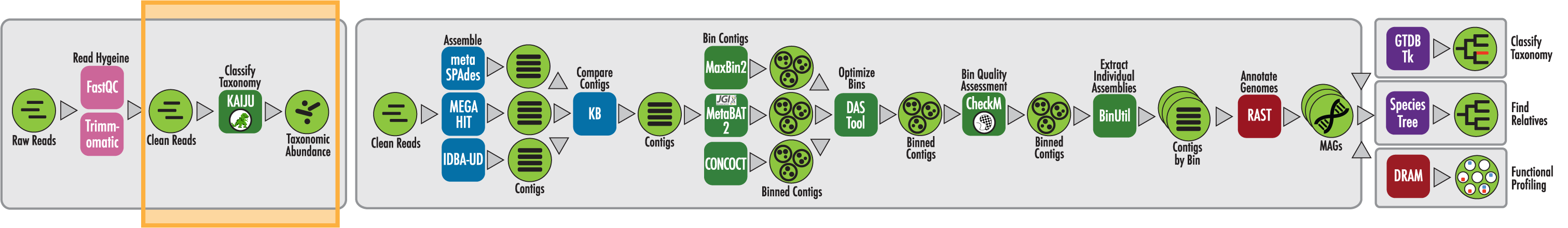
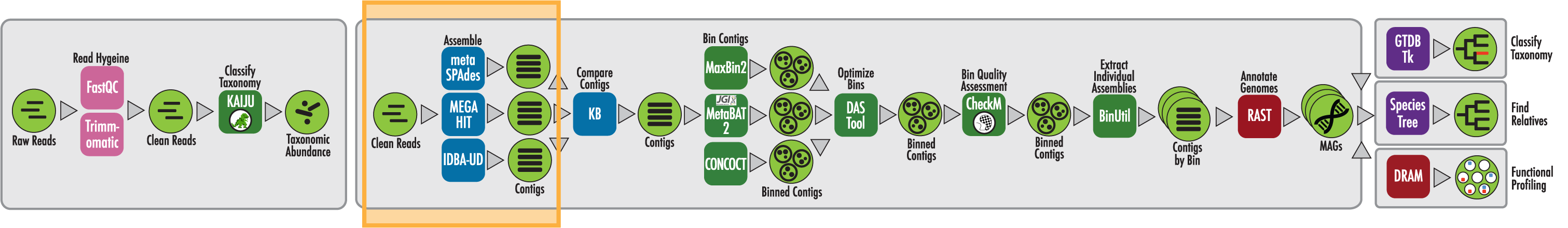
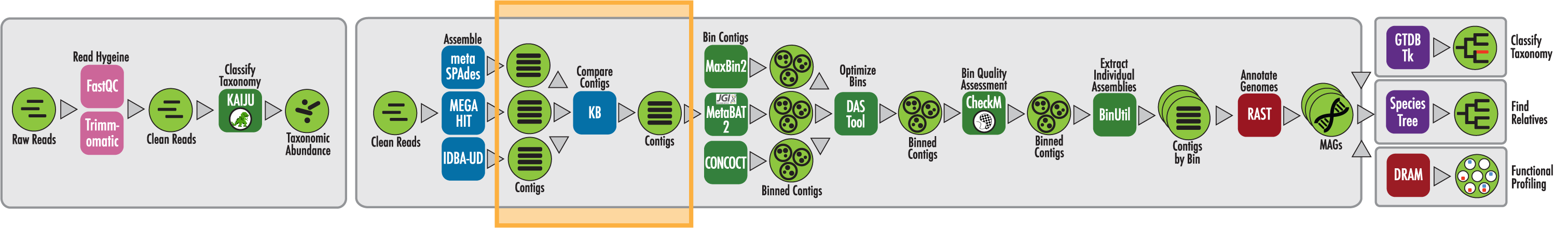
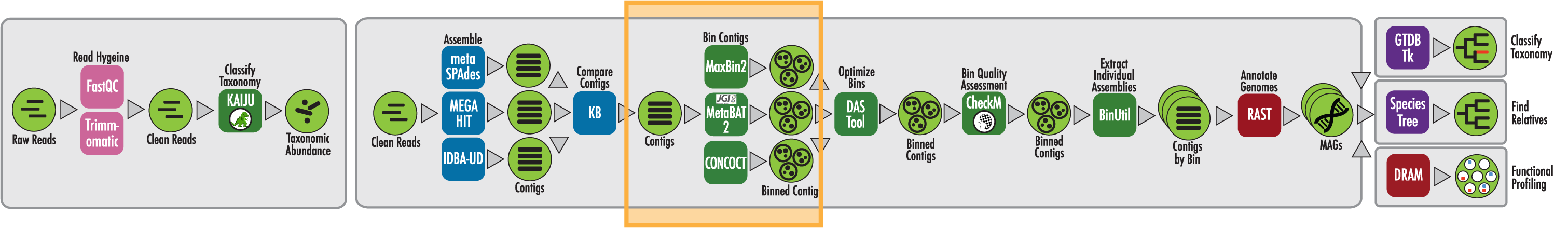
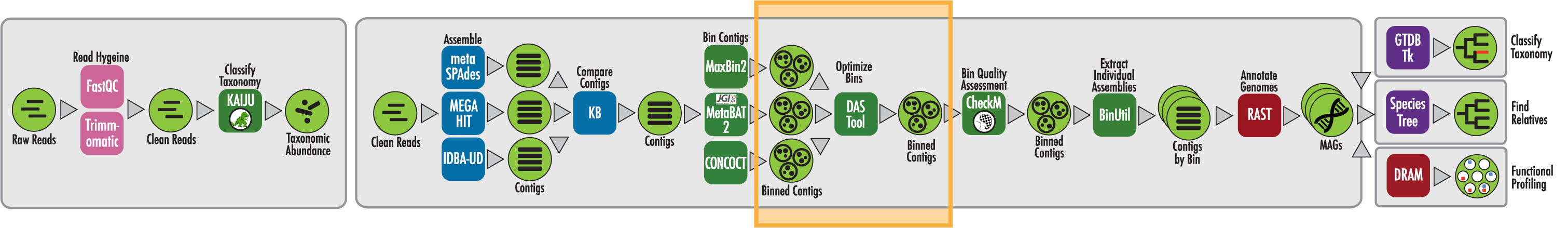
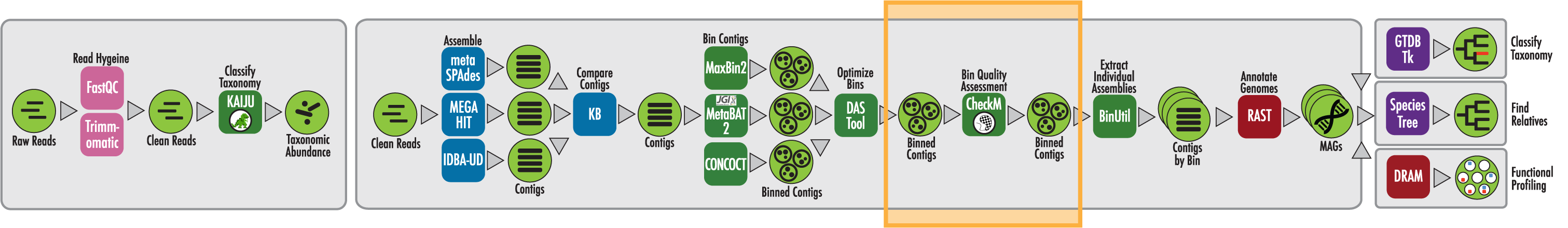
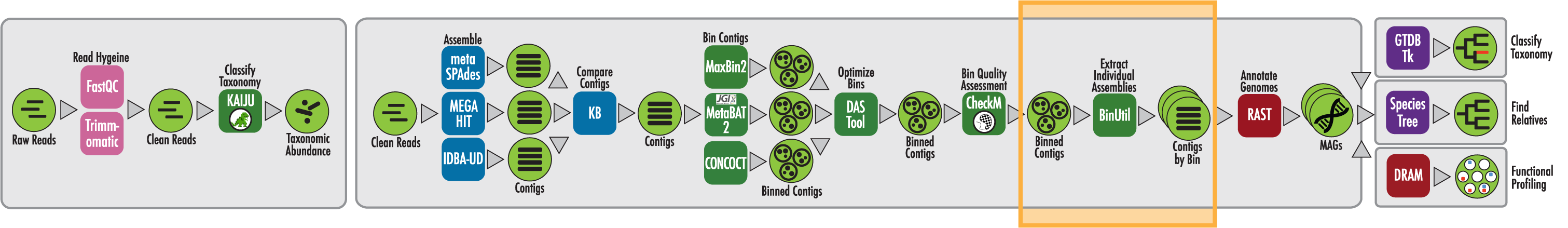
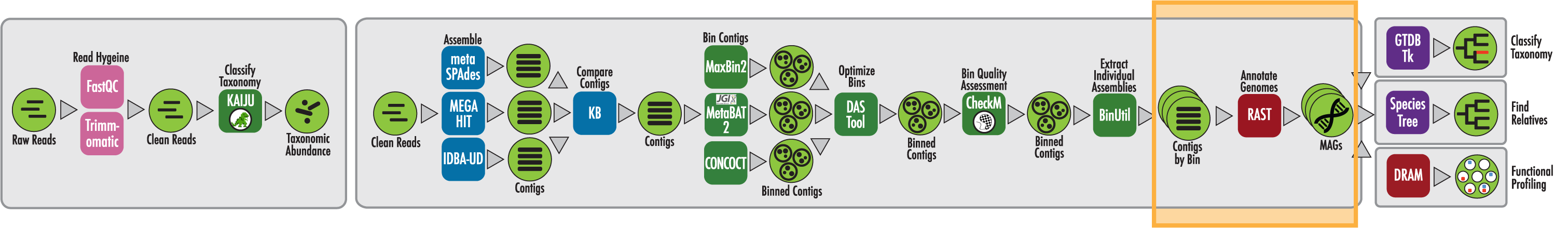
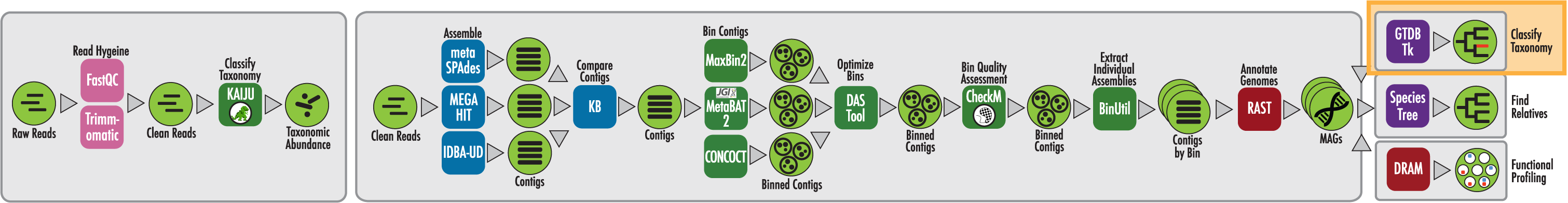
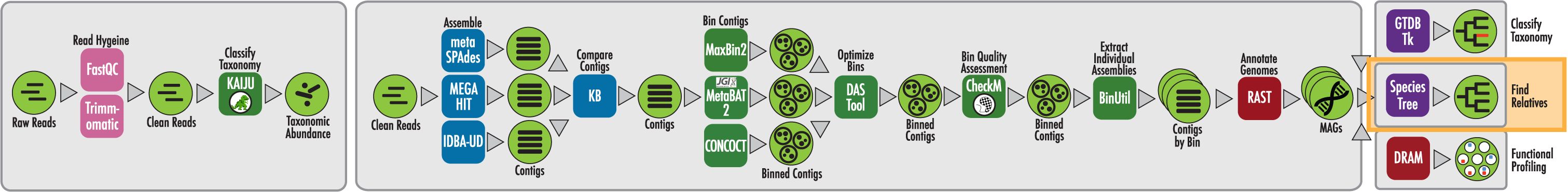
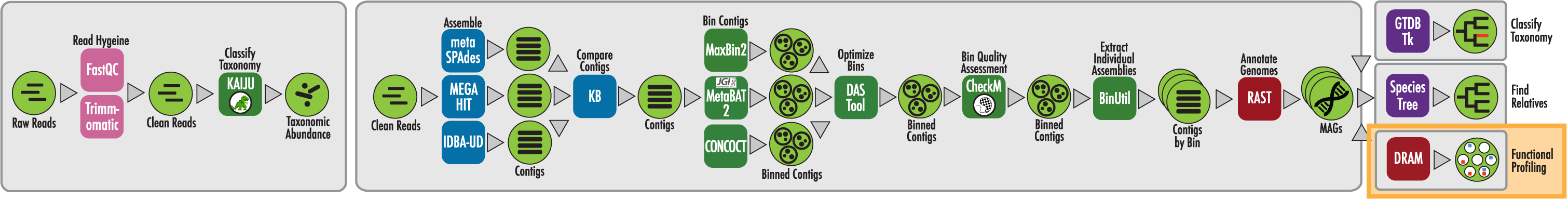
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 72 contigs containing 3555162 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3672 new features were called, of which 357 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3315
Non-coding crispr_array 1
Non-coding crispr_repeat 157
Non-coding crispr_spacer 156
Non-coding rna 43
Overall, the genes have 1814 distinct functions.
The genes include 1750 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 916 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.047.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 27 contigs containing 2818397 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2628 new features were called, of which 32 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2596
Non-coding rna 32
Overall, the genes have 1354 distinct functions.
The genes include 1273 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 781 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.025.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 128 contigs containing 4423359 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3762 new features were called, of which 45 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3717
Non-coding crispr_array 1
Non-coding crispr_repeat 7
Non-coding crispr_spacer 6
Non-coding repeat 2
Non-coding rna 29
Overall, the genes have 1716 distinct functions.
The genes include 1797 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 859 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.077.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 8 contigs containing 3009503 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3025 new features were called, of which 49 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2976
Non-coding repeat 2
Non-coding rna 47
Overall, the genes have 1729 distinct functions.
The genes include 1580 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 979 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.037.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 664 contigs containing 4711183 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 4830 new features were called, of which 68 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 4762
Non-coding repeat 44
Non-coding rna 24
Overall, the genes have 1699 distinct functions.
The genes include 2025 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 881 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.033.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 57 contigs containing 3885231 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 4110 new features were called, of which 527 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3583
Non-coding crispr_array 3
Non-coding crispr_repeat 233
Non-coding crispr_spacer 230
Non-coding repeat 12
Non-coding rna 49
Overall, the genes have 1323 distinct functions.
The genes include 2209 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 815 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.078.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 69 contigs containing 2896910 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2798 new features were called, of which 34 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2764
Non-coding repeat 2
Non-coding rna 32
Overall, the genes have 1272 distinct functions.
The genes include 1291 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 715 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.014.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 62 contigs containing 4602386 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 4072 new features were called, of which 36 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 4036
Non-coding rna 36
Overall, the genes have 1585 distinct functions.
The genes include 1883 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 885 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.044.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 65 contigs containing 2921546 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2983 new features were called, of which 93 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2890
Non-coding crispr_array 1
Non-coding crispr_repeat 25
Non-coding crispr_spacer 24
Non-coding repeat 2
Non-coding rna 41
Overall, the genes have 1916 distinct functions.
The genes include 1510 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1033 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.053.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 225 contigs containing 4363961 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 4884 new features were called, of which 346 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 4538
Non-coding crispr_array 3
Non-coding crispr_repeat 144
Non-coding crispr_spacer 141
Non-coding repeat 16
Non-coding rna 42
Overall, the genes have 2572 distinct functions.
The genes include 1868 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1157 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.020.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 498 contigs containing 4388328 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 4214 new features were called, of which 99 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 4115
Non-coding repeat 71
Non-coding rna 28
Overall, the genes have 1780 distinct functions.
The genes include 1836 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 873 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.058.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 37 contigs containing 4214068 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 4295 new features were called, of which 352 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3943
Non-coding crispr_array 4
Non-coding crispr_repeat 151
Non-coding crispr_spacer 147
Non-coding repeat 11
Non-coding rna 39
Overall, the genes have 2037 distinct functions.
The genes include 1856 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1124 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.067.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 326 contigs containing 3069604 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3116 new features were called, of which 33 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3083
Non-coding repeat 2
Non-coding rna 31
Overall, the genes have 1877 distinct functions.
The genes include 1566 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1036 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.028.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 107 contigs containing 3853049 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3907 new features were called, of which 60 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3847
Non-coding repeat 21
Non-coding rna 39
Overall, the genes have 1940 distinct functions.
The genes include 1876 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1082 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.039.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 138 contigs containing 4543190 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3793 new features were called, of which 66 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3727
Non-coding crispr_array 1
Non-coding crispr_repeat 3
Non-coding crispr_spacer 2
Non-coding repeat 28
Non-coding rna 32
Overall, the genes have 1713 distinct functions.
The genes include 1833 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 848 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.065.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 164 contigs containing 3174826 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3035 new features were called, of which 46 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2989
Non-coding repeat 9
Non-coding rna 37
Overall, the genes have 1442 distinct functions.
The genes include 1580 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 825 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.059.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 45 contigs containing 2474027 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2241 new features were called, of which 37 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2204
Non-coding rna 37
Overall, the genes have 1131 distinct functions.
The genes include 1099 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 671 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.062.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 107 contigs containing 3093537 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2941 new features were called, of which 46 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2895
Non-coding repeat 2
Non-coding rna 44
Overall, the genes have 1669 distinct functions.
The genes include 1565 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 992 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.005.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 61 contigs containing 2796035 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2710 new features were called, of which 47 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2663
Non-coding repeat 8
Non-coding rna 39
Overall, the genes have 1888 distinct functions.
The genes include 1385 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1104 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.029.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 84 contigs containing 1834279 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 1841 new features were called, of which 43 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 1798
Non-coding repeat 8
Non-coding rna 35
Overall, the genes have 1070 distinct functions.
The genes include 1022 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 674 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.004.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 402 contigs containing 4749785 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 5070 new features were called, of which 53 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 5017
Non-coding repeat 12
Non-coding rna 41
Overall, the genes have 2756 distinct functions.
The genes include 1976 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1103 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.043.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 74 contigs containing 2343119 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2372 new features were called, of which 45 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2327
Non-coding repeat 6
Non-coding rna 39
Overall, the genes have 1708 distinct functions.
The genes include 1314 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1029 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.011.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 221 contigs containing 3717720 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3698 new features were called, of which 172 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3526
Non-coding crispr_array 2
Non-coding crispr_repeat 66
Non-coding crispr_spacer 64
Non-coding repeat 6
Non-coding rna 34
Overall, the genes have 1662 distinct functions.
The genes include 1779 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 868 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.003.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 48 contigs containing 3936667 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3528 new features were called, of which 63 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3465
Non-coding repeat 26
Non-coding rna 37
Overall, the genes have 1607 distinct functions.
The genes include 1617 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 877 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.013.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 60 contigs containing 3633522 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3398 new features were called, of which 213 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3185
Non-coding crispr_array 2
Non-coding crispr_repeat 84
Non-coding crispr_spacer 82
Non-coding repeat 8
Non-coding rna 37
Overall, the genes have 1560 distinct functions.
The genes include 1670 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 889 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.057.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 27 contigs containing 4247528 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3765 new features were called, of which 40 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3725
Non-coding rna 40
Overall, the genes have 1689 distinct functions.
The genes include 1765 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 898 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.056.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 87 contigs containing 1907535 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 1999 new features were called, of which 102 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 1897
Non-coding crispr_array 1
Non-coding crispr_repeat 38
Non-coding crispr_spacer 37
Non-coding rna 26
Overall, the genes have 1161 distinct functions.
The genes include 1125 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 773 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.041.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 75 contigs containing 3259393 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2923 new features were called, of which 40 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2883
Non-coding rna 40
Overall, the genes have 1216 distinct functions.
The genes include 1538 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 721 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.052.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 34 contigs containing 2315542 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2279 new features were called, of which 44 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2235
Non-coding repeat 6
Non-coding rna 38
Overall, the genes have 1213 distinct functions.
The genes include 1126 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 705 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.080.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 377 contigs containing 2383018 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2615 new features were called, of which 143 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2472
Non-coding crispr_array 2
Non-coding crispr_repeat 30
Non-coding crispr_spacer 28
Non-coding repeat 50
Non-coding rna 33
Overall, the genes have 1051 distinct functions.
The genes include 1410 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 700 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.063.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 29 contigs containing 5288769 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 5355 new features were called, of which 285 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 5070
Non-coding crispr_array 4
Non-coding crispr_repeat 110
Non-coding crispr_spacer 106
Non-coding repeat 18
Non-coding rna 47
Overall, the genes have 2255 distinct functions.
The genes include 2512 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1167 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.021.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 47 contigs containing 2340301 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2450 new features were called, of which 104 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2346
Non-coding crispr_array 1
Non-coding crispr_repeat 33
Non-coding crispr_spacer 32
Non-coding rna 38
Overall, the genes have 1128 distinct functions.
The genes include 1234 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 795 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.018.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 41 contigs containing 3018906 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3161 new features were called, of which 489 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2672
Non-coding crispr_array 4
Non-coding crispr_repeat 222
Non-coding crispr_spacer 218
Non-coding repeat 2
Non-coding rna 43
Overall, the genes have 1690 distinct functions.
The genes include 1487 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 1012 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.098.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 108 contigs containing 1972189 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 2038 new features were called, of which 35 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 2003
Non-coding rna 35
Overall, the genes have 1158 distinct functions.
The genes include 1134 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 751 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.076.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 98 contigs containing 4844810 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 4244 new features were called, of which 45 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 4199
Non-coding repeat 2
Non-coding rna 43
Overall, the genes have 1826 distinct functions.
The genes include 2102 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 922 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.042.fasta_assembly succeeded!
The RAST algorithm was applied to annotating a genome sequence comprised of 31 contigs containing 3906929 nucleotides.
No initial gene calls were provided.
Standard features were called using: glimmer3; prodigal.
A scan was conducted for the following additional feature types: rRNA; tRNA; selenoproteins; pyrrolysoproteins; repeat regions; crispr.
The genome features were functionally annotated using the following algorithm(s): Kmers V2; Kmers V1; protein similarity.
In addition to the remaining original 0 coding features and 0 non-coding features, 3707 new features were called, of which 203 are non-coding.
Output genome has the following feature types:
Coding gene 3504
Non-coding crispr_array 1
Non-coding crispr_repeat 83
Non-coding crispr_spacer 82
Non-coding repeat 4
Non-coding rna 33
Overall, the genes have 1465 distinct functions.
The genes include 1693 genes with a SEED annotation ontology across 852 distinct SEED functions.
The number of distinct functions can exceed the number of genes because some genes have multiple functions.
Bin.061.fasta_assembly succeeded!